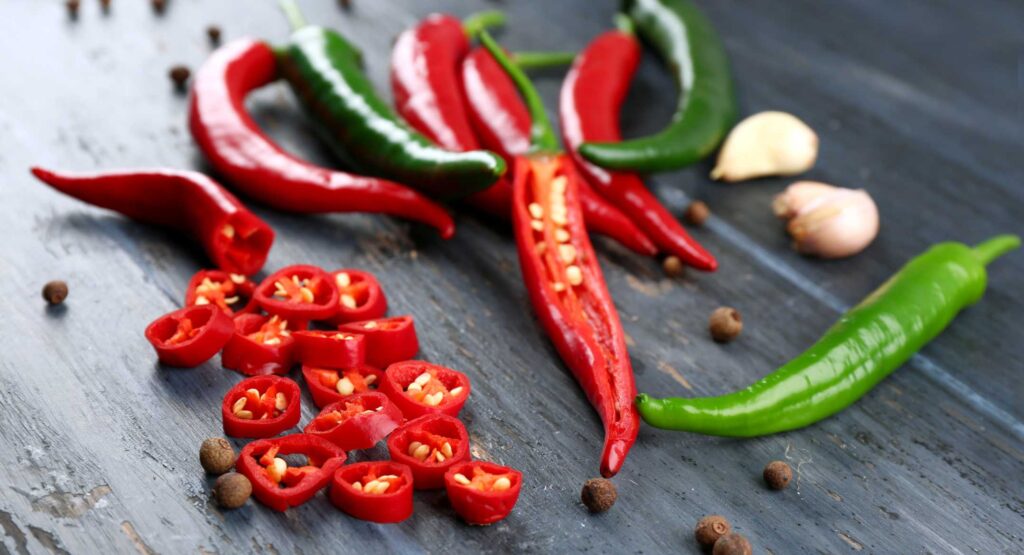
Capsaicin
TYPE OF INGREDIENT
Anti-pruritic, pain-reducing agent
COMMONLY FOUND IN
Creams, patches
WHAT ARE THE BENEFITS OF CAPSAICIN?
Capsaicin has been showing to be useful for the reduction of pain and itching, particularly in patients with diabetes or other neuropathic pain and those with pruritus, especially brachioradial pruritus.
WHAT IS CAPSAICIN?
Capsaicin is a derivative of chili peppers and acts on vanilloid receptors of sensory nerves, through which it is thought to reduce sensory innervation, ultimately reducing pain and itch through these receptor-blocking actions.

IS CAPSAICIN SAFE FOR ALL SKIN TYPES AND TONES?
Capsaicin is likely safe for all skin types and tones based on available data. However, patients with known hypersensitivity or other severe reactions to capsaicin should not use this product.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
There is minimal data on contraindications for the topical application of capsaicin. However, a report indicates that it should be used in limited concentrations as it can increase penetration of anti-inflammatory compounds in the skin and can thus be irritating.
Sources:
Final report on the safety assessment of capsicum annuum extract, capsicum annuum fruit extract, capsicum annuum resin, capsicum annuum fruit powder, capsicum frutescens fruit, capsicum frutescens fruit extract, capsicum frutescens resin, and capsaicin. Int J Toxicol. 2007;26 Suppl 1:3-106.
Parente, M. E., Ga´ Mbaro, A., & Solana, G. (2005). Study of sensory properties of emollients used in cosmetics and their correlation with physicochemical properties. International Journal of Cosmetic Science, 27(6), 354-354.
P. Anand, K. Bley, Topical capsaicin for pain management: therapeutic potential and mechanisms of action of the new high-concentration capsaicin 8% patch, BJA: British Journal of Anaesthesia, Volume 107, Issue 4, October 2011, Pages 490–502